Paying For Hours VS Paying For Business Value
The Traditional “Paying for Hours” Model
For decades, most software outsourcing and development projects have operated under a time-based pricing model — typically hourly or daily rates.
Common structure:
- Hourly rate: e.g., $50/hour for a developer
- Billing based on time logs or sprint hours
- Focus: Effort spent, not outcomes delivered
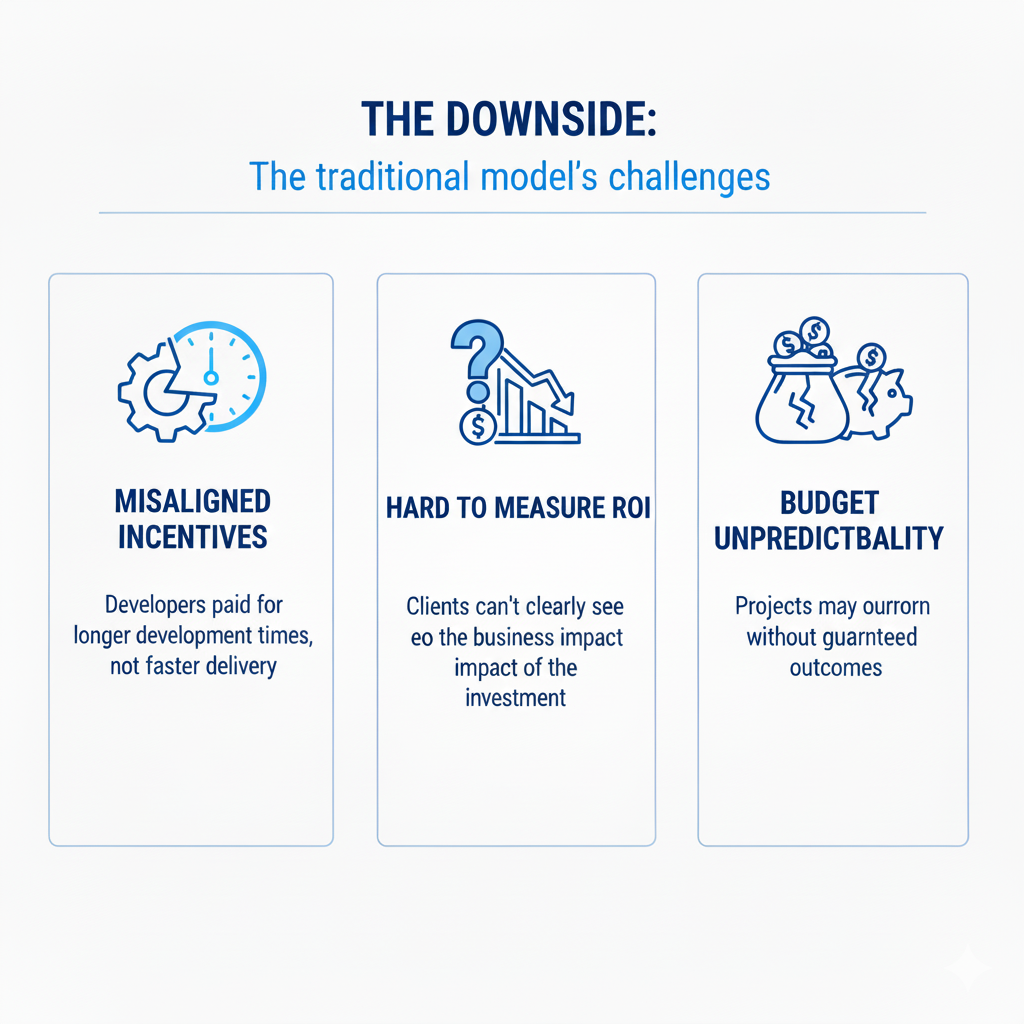
The downside:
- Misaligned incentives: Developers may get paid for longer development times, not faster delivery.
- Hard to measure ROI: Clients can’t clearly see the business impact of the investment.
- Budget unpredictability: Projects may overrun without guaranteed outcomes.
The Shift: From Hours to Delivered Business Value
The emerging model emphasizes “Paying for Delivered Business Value” — a paradigm shift where clients pay for outcomes, not effort. This approach ties pricing to the tangible impact or business results generated by the software solution.
What “Delivered Business Value” Means in Software Development
“Business value” can vary depending on the nature of the software or project, but it generally refers to measurable benefits that contribute to business goals.

Common forms of business value:
- Revenue impact — e.g., software that increases conversion rates or sales
- Efficiency gains — automation that reduces manual work or time spent
- Cost reduction — migrating to cloud or optimizing infrastructure
- User growth or engagement — features that boost retention or usage
- Strategic enablement — enabling new business capabilities
In this model, payment milestones or pricing structures are based on value creation metrics rather than hours worked.
How This Works for Software Outsourcing Companies
For outsourcing companies, the model shifts from selling time and skill to selling results and expertise.
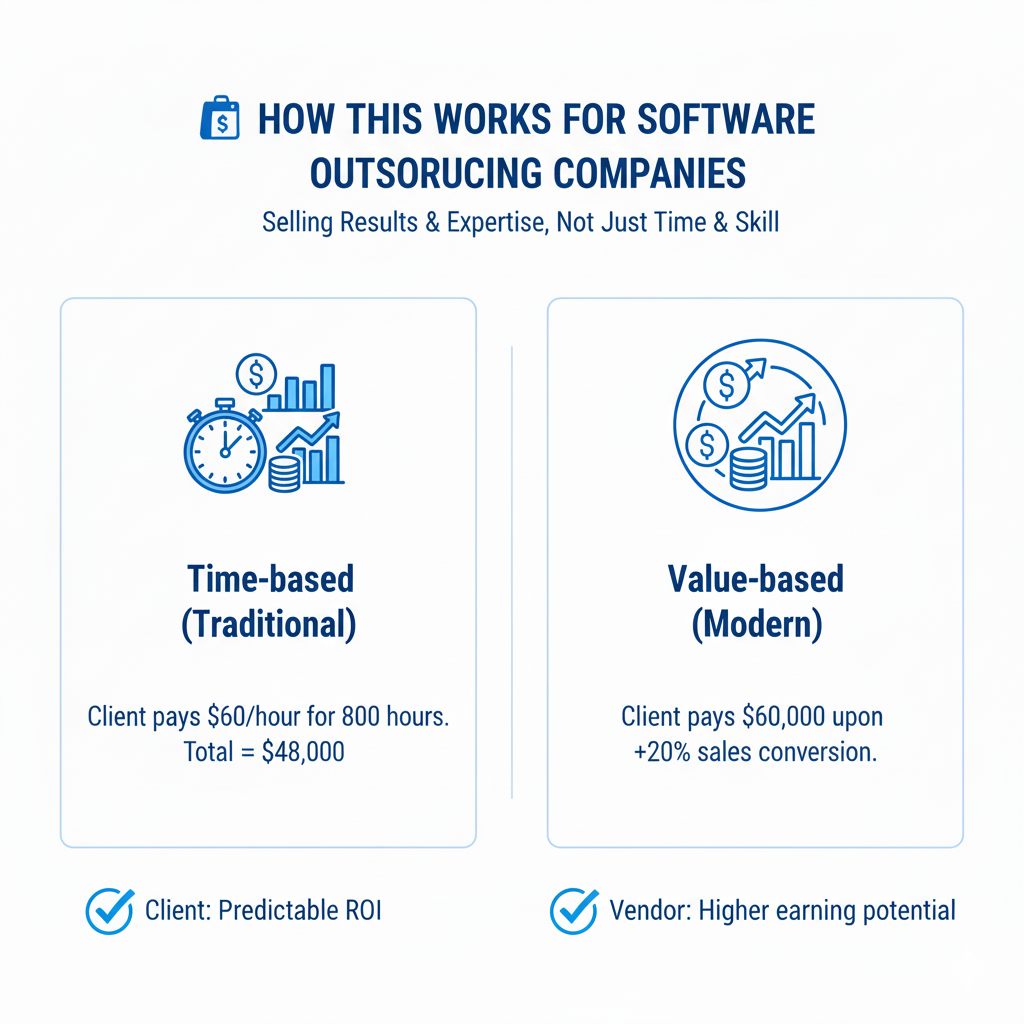
Example Scenario 1: Traditional vs. Value-Based Model
Scenario
Time-based (Traditional):
A U.S. retail company hires your outsourcing team to build an e-commerce platform. You charge $60/hour for 800 hours. Total = $48,000.
Value-based (Modern):
Instead of hourly rates, you propose: “We’ll deliver a platform that improves online sales conversion by at least 20%. Our fee is $60,000, payable upon achieving that result.”
Benefits for client: Predictable ROI and measurable results.
Benefits for vendor: Higher earning potential when delivering real value efficiently.
How This Works for Software Product Companies
For companies that build software products (SaaS or enterprise tools), the concept translates into value-based pricing — charging based on impact or usage, not just features or licenses.
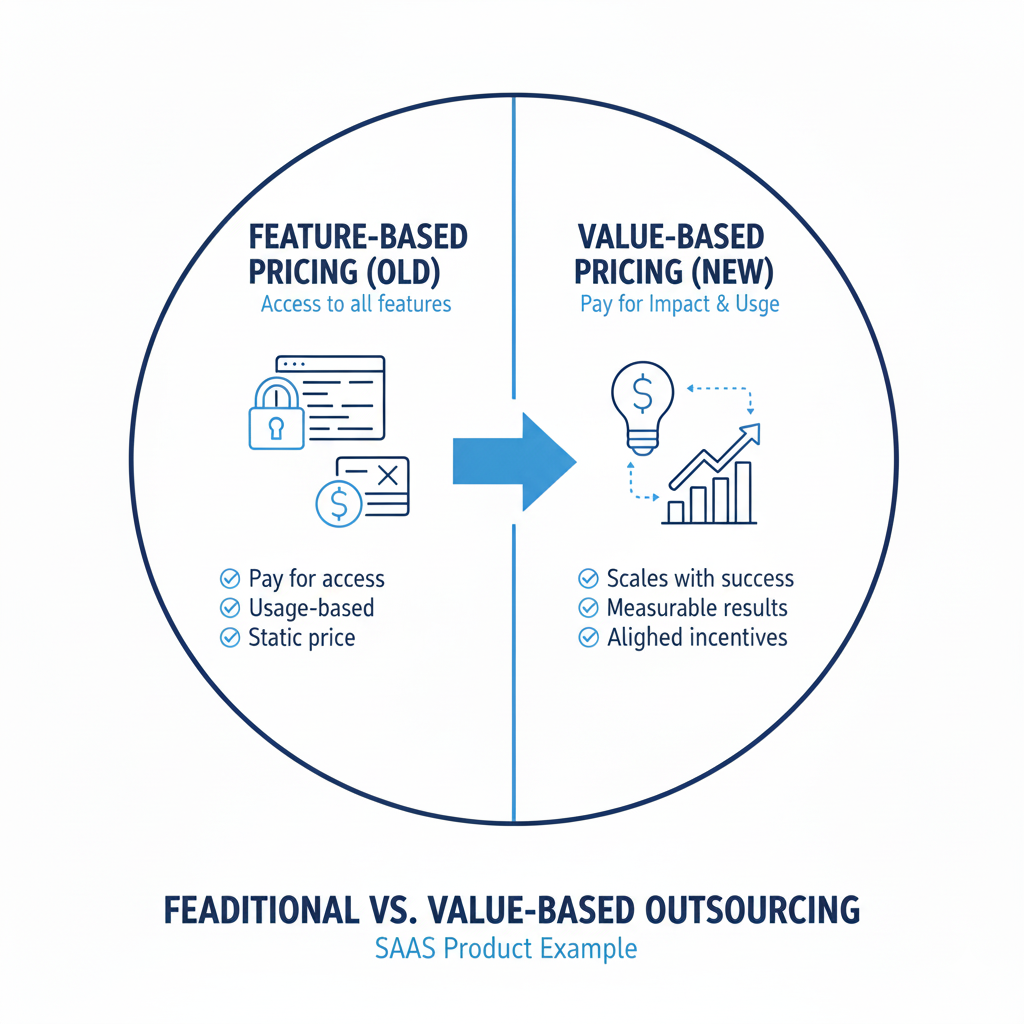
Example Scenario 2: SaaS Product Example Model
Scenario
Feature-based pricing (Old):
Your analytics SaaS charges $500/month for access to all dashboards.
Value-based pricing (New):
You charge based on the number of leads generated or revenue insights enabled — e.g., 1% of the revenue the software helps uncover.
✅ Benefit: Customers feel they’re paying for tangible gains, not abstract usage.
✅ Company gain: Pricing scales with the customer’s success.
Implementation Strategies for Outsourcing Firms
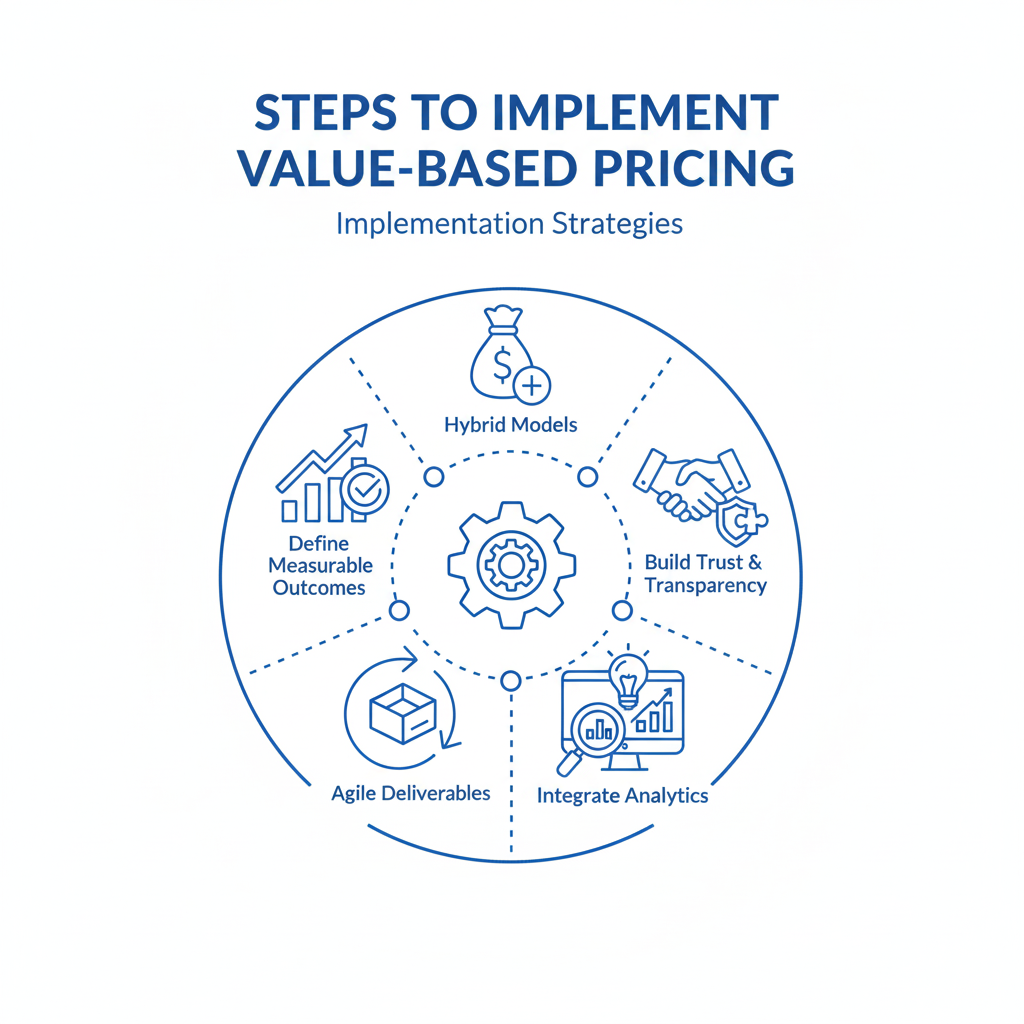
Steps to Implement Value-Based Pricing
1. Define clear measurable outcomes
Tie pricing to specific, measurable metrics like conversion, retention, uptime, or delivery time.
Example: “Reduce processing time by 40%” or “Launch MVP within 6 weeks.”
2. Create hybrid models
Start with a base development fee (to cover costs) + performance-based bonuses.
Example: $30,000 base + $10,000 bonus upon achieving the business metric.
3. Build trust and transparency
Clients must trust your expertise and delivery.
Share past success stories and value outcomes achieved for similar clients.
4. Use agile deliverables
Deliver value in sprints with measurable outputs (MVPs, automation savings, etc.)
5. Integrate analytics
Use analytics dashboards to track metrics and prove delivered business value.
Benefits of Shifting to Value-Based Pricing
For companies that build software products (SaaS or enterprise tools), the concept translates into value-based pricing — charging based on impact or usage, not just features or licenses.
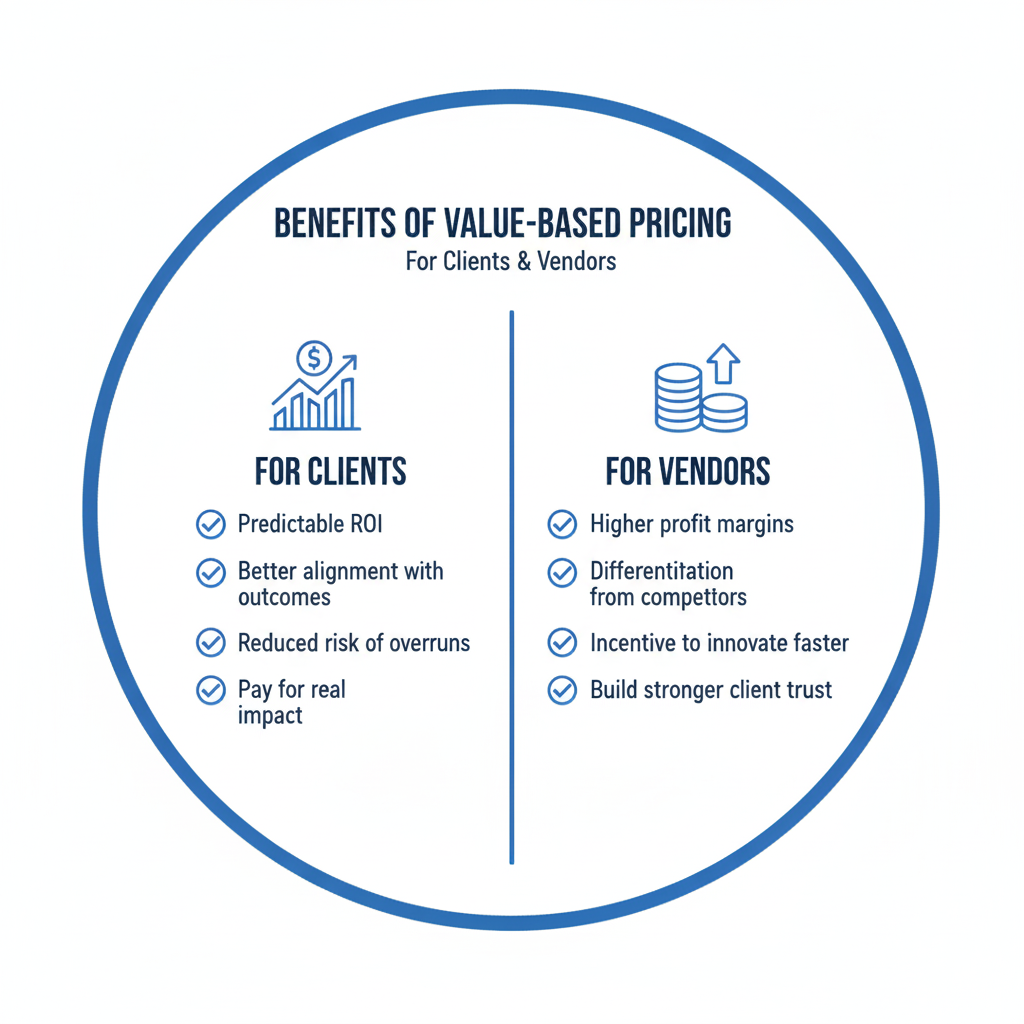
Benefits of Value-Based Pricing
For Clients
- Predictable ROI
- Better alignment with outcomes
- Reduced risk of overruns
- Pay for real impact
For Vendor
- Higher profit margins
- Differentiation from competitors
- Incentive to innovate faster
- Build stronger, long-term client trust
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
For companies that build software products (SaaS or enterprise tools), the concept translates into value-based pricing — charging based on impact or usage, not just features or licenses.
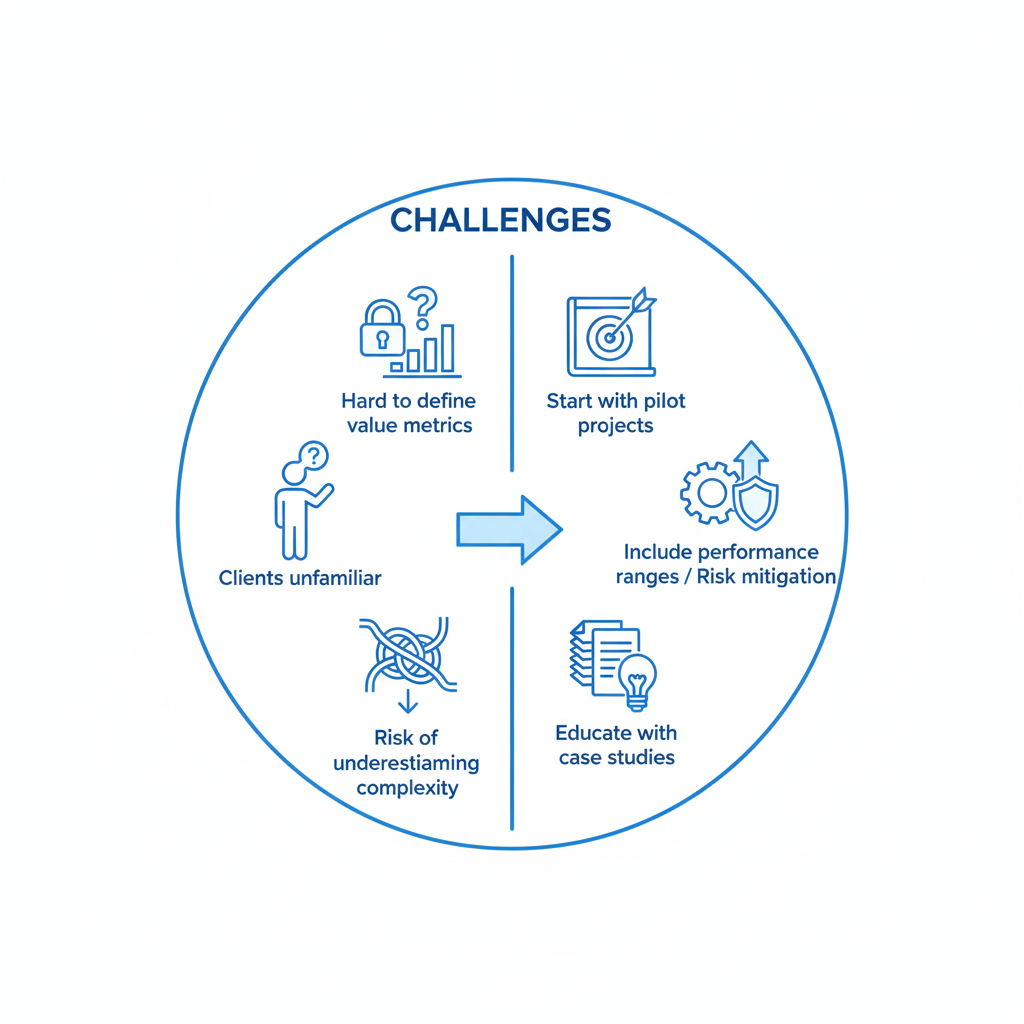
Challenges & Solutions
Challenge
Hard to define value metrics upfront
Solution
Start with pilot projects or hybrid pricing models
Clients unfamiliar with the concept
Educate with case studies showing ROI
Risk of underestimating delivery complexity
Include performance ranges or tiered value targets
Conclusion: The Future of Software Partnerships
The shift from “Paying for Hours” to “Paying for Delivered Business Value” represents a deeper maturity in the software ecosystem. It transforms outsourcing firms and product companies from service providers into strategic partners — rewarded for impact, not just effort. As more businesses demand measurable ROI, those who can define, deliver, and demonstrate business value will lead the next wave of software innovation.
